Is your current router holding you back?
Do you know what speeds
your router can achieve?
Not all routers can keep up. It’s important to double check what Wi-Fi generation your router supports, as only the latest Wi-Fi generations will allow you to handle higher download speeds.
If your router doesn’t support the latest Wi-Fi standards, your maximum speeds will be limited, regardless of your internet plan.
Here’s a helpful table from nbn® showing the common Wi-Fi generations and their typical maximum achievable Wi-Fi speeds:
| Wi-Fi generation | Typical maximum Wi-Fi speeds | Approximate year of release |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) |
Over 1Gbps | 2024 |
| Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) |
Up to 1Gbps | 2019 |
| Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) |
Up to 500Mbps | 2013 |
| Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) |
Up to 100Mbps | 2009 |
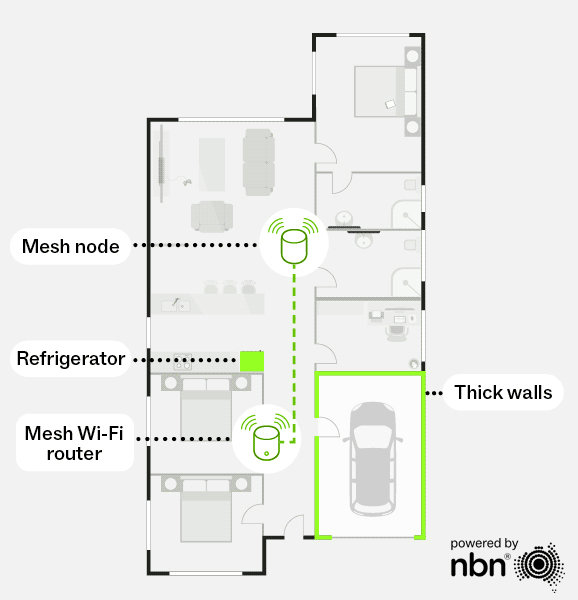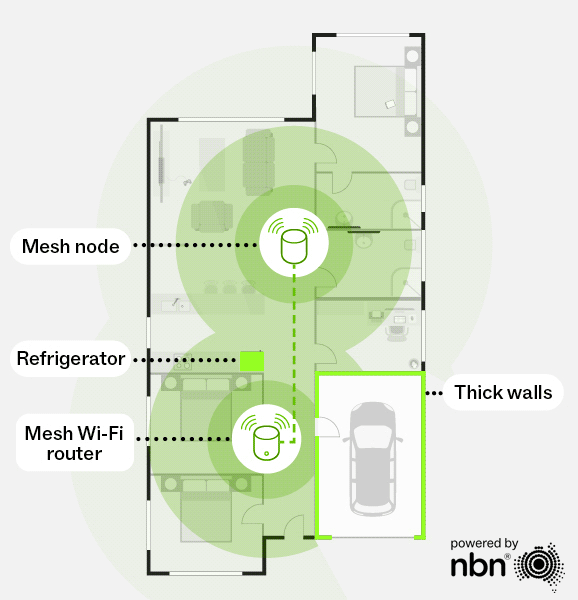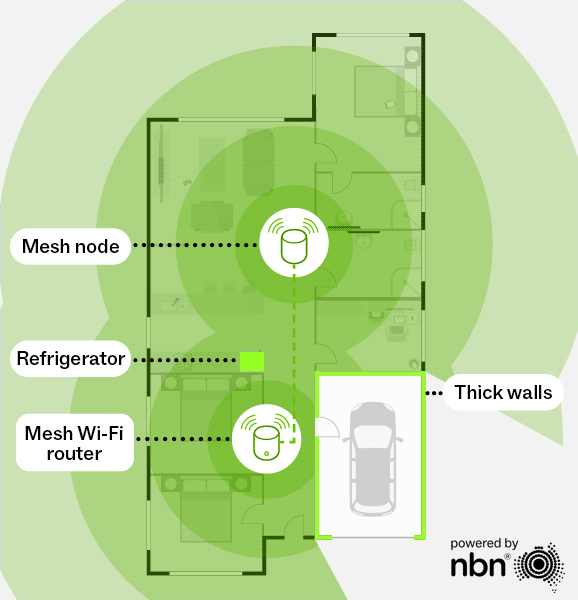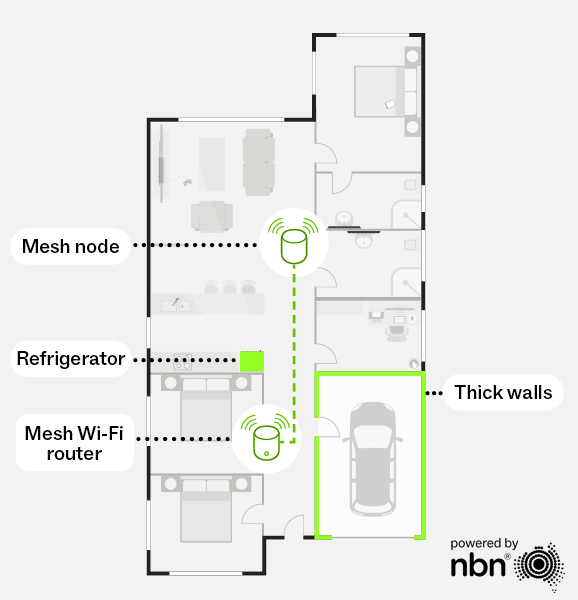
Mesh Wi-Fi routers
If you live in a larger, multi-storey home or one with thick walls or metal-heavy construction, a mesh Wi-Fi system might be the better choice compared to a single router.
Mesh Wi-Fi uses multiple routers (or “nodes”) working together to deliver seamless, whole-home coverage. Unlike a single router that can leave dead zones, a mesh network will use these nodes to extend the Wi-Fi signal across your home without sacrificing speed. As you move around, your devices automatically connect to the strongest signal, providing a smooth and consistent experience.
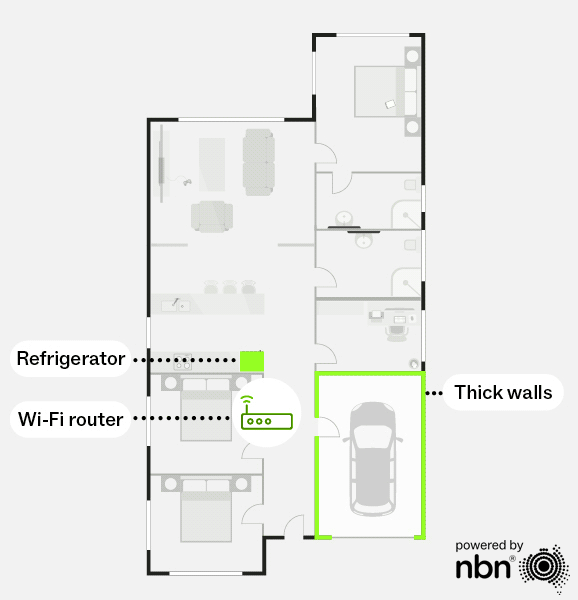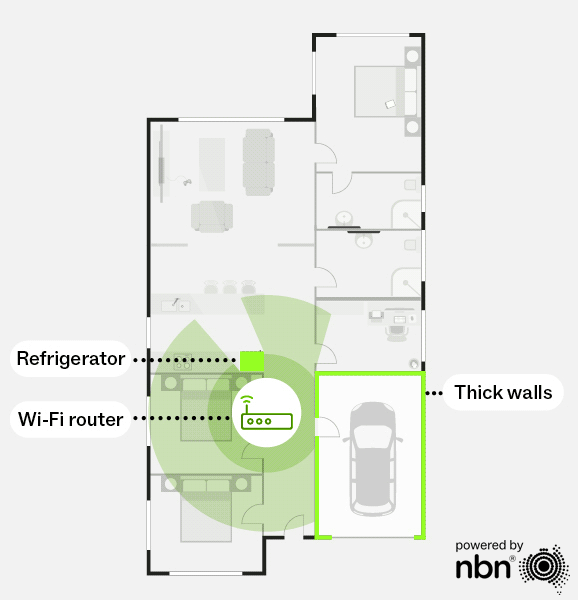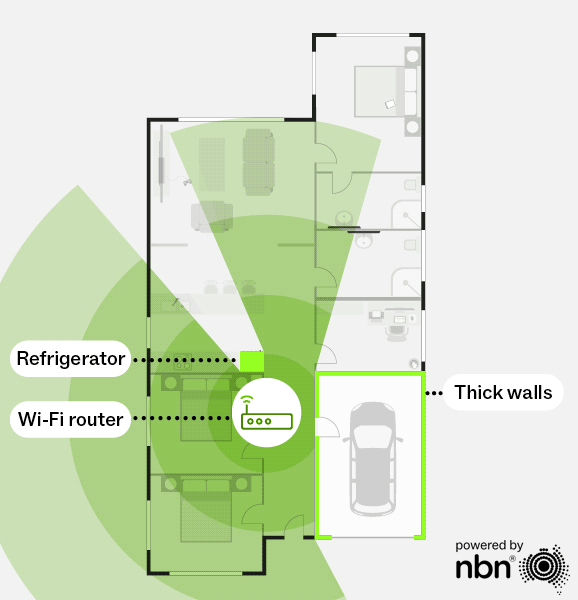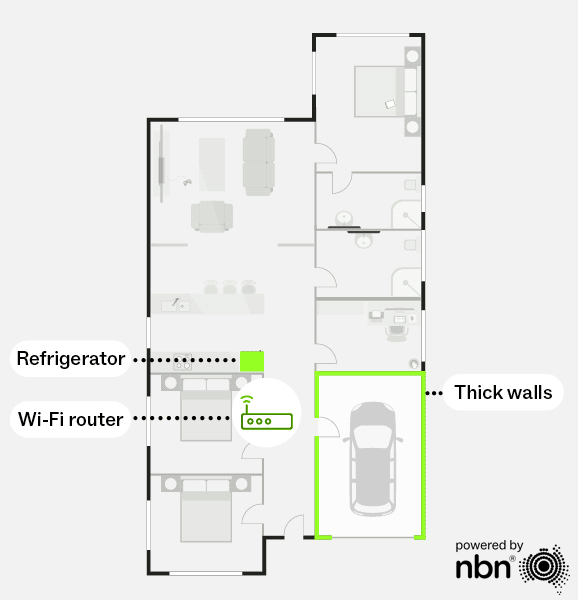
Without a mesh network
With a mesh network
Don’t forget to check your ports
When choosing the right router, it’s not just about Wi-Fi speeds and coverage. The ports on the back of your router matter too. Here’s what to look for:
WAN vs LAN ports: what’s the difference?
- WAN Port (Wide Area Network):
This is where your internet connection plugs in, usually via an Ethernet cable from your modem, or nbn® connection box. Think of it as your router’s “gateway” to the internet. - LAN Ports (Local Area Network):
These are used to connect your devices, such as PCs, gaming consoles, or smart TVs directly to your router. They allow for a faster, more stable connection compared to Wi-Fi.
Different port speeds and why they matter
- GbE Ports (Gigabit Ethernet):
Ideal for today’s internet speeds and modern devices. If you’re on a fast internet plan, you should ensure your router has gigabit ports to get the full benefit.
Example: If you’re on a 2000Mbps plan, you will need a Wi-Fi 7 router with 2.5GbE ports to fully support your internet plan’s speed.
- FE Ports (Fast Ethernet):
These are outdated and will limit the speeds you can receive (up to 100Mbps), even if your internet plan is faster.
| Plan download speed | Minimum WAN port and cable speeds | Minimum LAN port and cable speeds |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 100Mbps | Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) | Fast Ethernet (FE) |
| 100Mbps – close to 1Gbps | Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) | Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) |
| 1Gbps – 2Gbps | 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet (2.5GbE) | 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet (2.5GbE) |
Need help picking the right router? We’ve got you
Leaptel provides various routers, including the eero 7 and eero pro 7, featuring TrueMesh technology, Wi-Fi 7 support, and multi-gigabit ports. These ensure you get the most out of your home internet plan, regardless of your current plan.
And if you ever get stuck, simply reach out to our Australian-based support team, and we’ll be more than happy to help you choose the right router for your home internet needs.